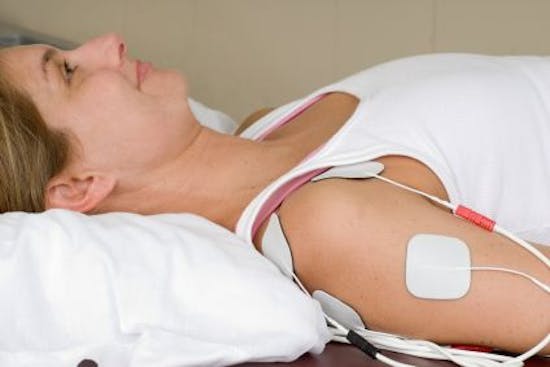
Interferential ultrasound therapy is a form of electrotherapy used in physiotherapy to help relieve pain and promote tissue healing. It combines the principles of ultrasound therapy with the benefits of electrical stimulation. Here’s an overview of interferential ultrasound therapy:
How It Works:
Ultrasound: Like traditional ultrasound therapy, interferential ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves. These waves penetrate into the tissues, causing a gentle heating effect.
Interference Currents: In addition to ultrasound, interferential therapy involves the use of two medium-frequency electrical currents that “interfere” with each other where they cross paths within the body. These currents are typically at frequencies of 4,000 Hz and 4,400 Hz.
Frequency Crossing: The two currents are set at slightly different frequencies. When they cross paths, they produce a low-frequency current inside the body, which can have therapeutic effects.
Effects and Benefits:
Pain Relief:
Interferential ultrasound therapy helps to alleviate pain by:
- Stimulating the release of endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers.
- Blocking pain signals to the brain.
- Reduced Inflammation: The heating effect of ultrasound can help reduce inflammation and swelling in the tissues.
- Improved Blood Flow: By increasing blood flow to the area, it promotes healing and tissue repair.
Muscle Relaxation: The combination of ultrasound and electrical stimulation can help relax tight muscles and reduce muscle spasms.
Procedure:
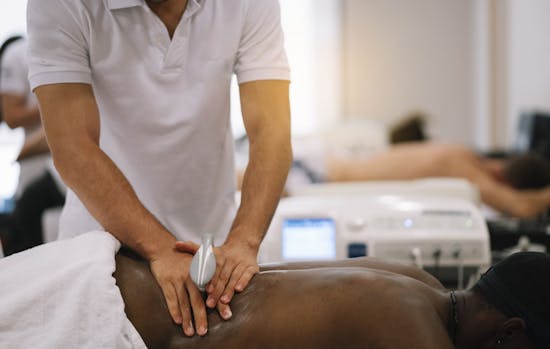
Preparation: The area to be treated is prepared by applying a conductive gel to ensure good contact between the skin and the ultrasound head.
Ultrasound Application:The physiotherapist moves the ultrasound head in a circular motion over the area being treated. This delivers the ultrasound waves into the tissues.
Electrodes Placement: Electrodes are placed on the skin around the treatment area to deliver the interference currents.
Treatment Duration: A typical session may last between 10 to 20 minutes, depending on the condition being treated and the therapist’s recommendations.
Conditions Treated:
Musculoskeletal Pain: Interferential ultrasound therapy is commonly used for conditions such as:
- Back pain
- Neck pain
- Shoulder pain
- Knee pain
- Sprains and strains
Soft Tissue Injuries: It can be beneficial for tendonitis, bursitis, and other soft tissue injuries.
Frequency and Duration:
The number of treatments and frequency will vary depending on the condition being treated.
A typical course of treatment may involve several sessions per week, gradually reducing as symptoms improve.
Conclusion:
Interferential ultrasound therapy is a valuable modality in physiotherapy, combining the benefits of ultrasound and electrical stimulation to provide pain relief, reduce inflammation, and promote tissue healing. It is generally considered safe and well-tolerated. If you are considering interferential ultrasound therapy, consult with a physiotherapist at Medhealth Physiotherapy to determine if it’s an appropriate option for your condition.
