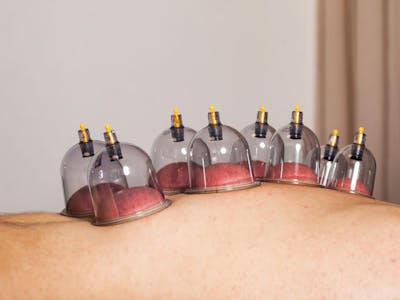
Cupping physiotherapy is a combination of traditional cupping therapy techniques with modern physiotherapy principles. It’s a practice where cupping therapy is integrated into physiotherapy treatments to help address various musculoskeletal issues, pain management, and rehabilitation. Here’s an overview:
Integration with Physiotherapy:
Musculoskeletal Conditions: Cupping physiotherapy is often used to complement traditional physiotherapy for conditions like back pain, neck pain, shoulder pain, and other musculoskeletal issues.
Myofascial Release: Cupping can be used to release tension and tightness in the muscles and fascia, aiding in improving range of motion and reducing pain.
Enhancing Blood Flow: By using cupping techniques, physiotherapists aim to improve blood circulation to specific areas, which can promote healing and reduce inflammation.
Techniques:
Dry Cupping: The cups are placed on the skin with suction, helping to lift the skin and tissues.
Movement Cupping: Cups are moved around the affected area to create a massage-like effect, improving blood flow and releasing tension.
Fire Cupping: Fire cupping is a traditional form of cupping therapy where glass cups are used along with fire to create suction on the skin.
Benefits:
Pain Relief: Cupping can help alleviate pain by releasing tight muscles and improving blood flow to the area.
Improved Flexibility: By releasing tension and tightness, cupping can improve range of motion and flexibility.
Improved Blood Flow: The suction created by fire cupping can promote better blood circulation to the area, aiding in healing and reducing inflammation.
Reduced Inflammation: The improved circulation can aid in reducing inflammation, which is beneficial for conditions like arthritis.
Enhanced Recovery: For athletes or individuals recovering from injuries, cupping physiotherapy can help speed up recovery times.
Relaxation: Many people find fire cupping to be relaxing, similar to a deep tissue massage.
Risks:
Bruising and Marks: Cupping can leave marks on the skin, which are not bruises but rather the result of suction on the capillaries. These marks typically fade within a few days.
Skin Irritation: There is a risk of skin irritation if the cups are left on for too long or if the skin is sensitive.
Considerations:
Individualized Treatment: Cupping physiotherapy should be tailored to the individual’s condition and needs, so it’s essential to consult with a trained physiotherapist.
Combination with Other Therapies: Cupping is often used in conjunction with other physiotherapy techniques such as exercises, manual therapy, and electrotherapy.
Conclusion:
Cupping physiotherapy offers an additional tool in the toolbox for physiotherapists to address a range of musculoskeletal issues and pain conditions. It is safe and effective part of a comprehensive treatment plan. As with any therapy, it’s essential to discuss the options with physiotherapist at Medhealth Physiotherapy to determine if cupping is suitable for your specific needs.